Read from Firestore
Add to favorites
Install Cloud Firestore in your application to fetch and read data from a collection
SwiftUI Advanced Handbook
1
Firebase Auth
8:18
2
Read from Firestore
8:01
3
Write to Firestore
5:35
4
Join an Array of Strings
3:33
5
Data from JSON
5:08
6
HTTP Request
6:31
7
WKWebView
5:25
8
Code Highlighting in a WebView
5:11
9
Test for Production in the Simulator
1:43
10
Debug Performance in a WebView
1:57
11
Debug a Crash Log
2:22
12
Simulate a Bad Network
2:11
13
Archive a Build in Xcode
1:28
14
Apollo GraphQL Part I
6:21
15
Apollo GraphQL Part 2
6:43
16
Apollo GraphQL Part 3
5:08
17
Configuration Files in Xcode
4:35
18
App Review
5:43
19
ImagePicker
5:06
20
Compress a UIImage
3:32
21
Firebase Storage
11:11
22
Search Feature
9:13
23
Push Notifications Part 1
5:59
24
Push Notifications Part 2
6:30
25
Push Notifications Part 3
6:13
26
Network Connection
6:49
27
Download Files Locally Part 1
6:05
28
Download Files Locally Part 2
6:02
29
Offline Data with Realm
10:20
30
HTTP Request with Async Await
6:11
31
Xcode Cloud
9:23
32
SceneStorage and TabView
3:52
33
Network Connection Observer
4:37
34
Apollo GraphQL Caching
9:42
35
Create a model from an API response
5:37
36
Multiple type variables in Swift
4:23
37
Parsing Data with SwiftyJSON
9:36
38
ShazamKit
12:38
39
Firebase Remote Config
9:05
Note: If you haven't, I suggest reading the section about setting up Firebase Auth in your application. You must have Firebase available in your application, as well as a Firestore database in your project, in order to continue.
Setup
Enable Firestore in your application by navigating to the Cloud Firestore tab in Firebase. Then, click on Create database.

A modal will popup and ask if you want to start in production mode or test mode. Choose test mode for now. This will allow you to test Firestore freely, and you won't be blocked by permission rules. Click on Next.

Next, you'll need to choose where you want your Firestore server to be located. This cannot be changed afterwards, so select the one most appropriate to your current location. For me, I will keep nam5 (us-central). Finally, click on Enable.

FirestoreManager class
After your database is created, you can go to your Xcode project and create a file named FirestoreManager.swift. Import Firebase at the top of your file.
// FirestoreManager.swift
import FirebaseCreate a FirestoreManager class in this file.
// FirestoreManager.swift
import Firebase
class FirestoreManager: ObservableObject {
}Read a single document
Let's start by learning how to read a single Firestore document. Let's say only want to extract data from a restaurant called Pizza Mania (saved as PizzaMania in the Restaurants collection).
In the FirestoreManager class, create a @Published variable called restaurant. It'll be a String.
// FirestoreManager.swift
@Published var restaurant: String = ""Then, create your function fetchRestaurant to find a specific restaurant's data.
// FirestoreManager.swift
func fetchRestaurant() {
let db = Firestore.firestore()
let docRef = db.collection("Restaurants").document("PizzaMania")
docRef.getDocument { (document, error) in
guard error == nil else {
print("error", error ?? "")
return
}
if let document = document, document.exists {
let data = document.data()
if let data = data {
print("data", data)
self.restaurant = data["name"] as? String ?? ""
}
}
}
}In the code above, we are importing the Firestore database.
Then, we are specifying the reference of the document (docRef) we want to fetch data from.
Next, we will get the document with the .getDocument method from Firestore. If there's an error, we'll print the error and exit the function. If the document exists, we want to call the .data() to get the actual data, then printing on the console and saving it to the restaurant variable we created. If not, we will print Document does not exist in the console.
Call this function on init of the class.
// FirestoreManager.swift
init() {
fetchRestaurant()
}Loop through a collection
If you want to loop through the entire restaurant collection to get each document, the code will look a little different:
// FirestoreManager.swift
func fetchAllRestaurants() {
let db = Firestore.firestore()
db.collection("Restaurants").getDocuments() { (querySnapshot, error) in
if let error = error {
print("Error getting documents: \(error)")
} else {
for document in querySnapshot!.documents {
print("\(document.documentID): \(document.data())")
}
}
}
}In the code above, instead of getting a specific document, we will get all documents with .getDocuments(). Then, we are looping through each document in the querySnapshot's documents and printing it on the console.
You can also call this function on init of the class.
// FirestoreManager.swift
init() {
fetchAllRestaurants()
}Add environmentObjects
Add your class as an environmentObject in your ProjectNameApp.swift as well as your ContentView.
// ProjectNameApp.swift
import SwiftUI
import Firebase
@main
struct ProjectNameApp: App {
@StateObject var firestoreManager = FirestoreManager()
init() {
FirebaseApp.configure()
}
var body: some Scene {
WindowGroup {
ContentView()
.environmentObject(firestoreManager)
}
}
}// ContentView.swift
struct ContentView: View {
@EnvironmentObject var firestoreManager: FirestoreManager
// Some other code...
}Remember to add the environmentObject to your preview as well to make it work:
struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
ContentView()
.environmentObject(FirestoreManager())
}
}Display the data
To display the data in your View, simply call the firestoreManager.restaurant.
// ContentView.swift
var body: some View {
Text("My restaurant: \(firestoreManager.restaurant)")
.padding()
}Update Firestore permission rules
Once you're ready to release your app, remember to update your Firestore rules to protect your database and not allow anyone to read and write your database.
Navigate to Cloud Firestore and click on the Rules tab. There, you'll see the rules that are currently applied to your database. If you started in test mode, anyone will be able to read and write to your database for about a month after you created the database.
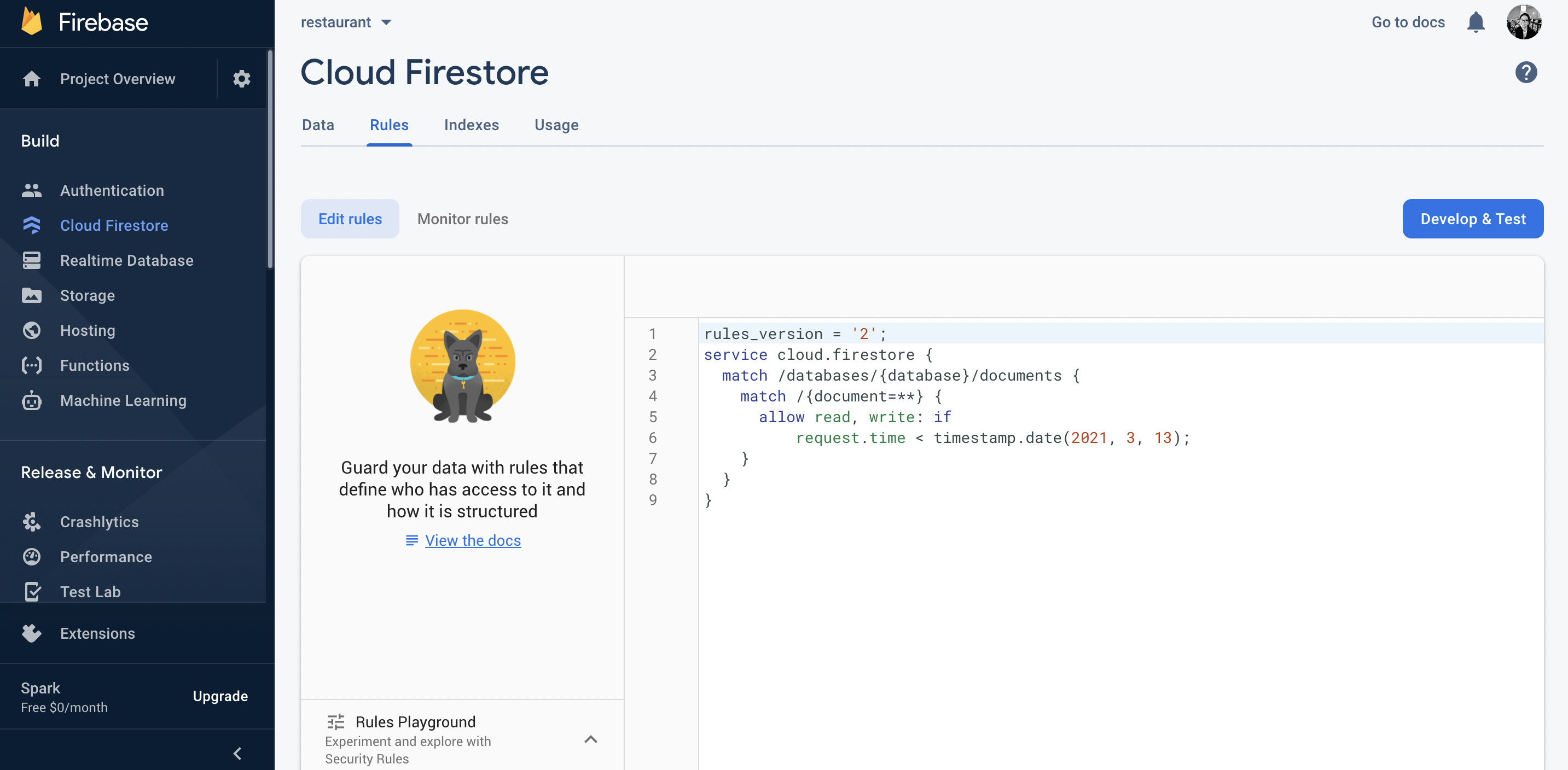
You want update the rules depending on how your users will interact with your database. Are they going to only read data? Will they also be able to write data?
In this case, our users are only allowed read the Restaurants collection from our database, so we will update the rules like so:
rules_version = '2';
service cloud.firestore {
match /databases/{database}/documents {
match /{Restaurants=**} {
allow read: if true;
}
}
}You can read more about Cloud Firestore Rules here.
Cloud Firestore Rules comes with a handy tool called Rules Playground, where you can test your rules before publishing them. Here, my simulated read passed, so I'll click on Publish and we're good to go!

Learn with videos and source files. Available to Pro subscribers only.
Purchase includes access to 50+ courses, 320+ premium tutorials, 300+ hours of videos, source files and certificates.
Templates and source code
Download source files
Download the videos and assets to refer and learn offline without interuption.
Design template
Source code for all sections
Video files, ePub and subtitles
Videos
Assets
ePub
Subtitles
1
Firebase Auth
How to install Firebase authentification to your Xcode project
8:18
2
Read from Firestore
Install Cloud Firestore in your application to fetch and read data from a collection
8:01
3
Write to Firestore
Save the data users input in your application in a Firestore collection
5:35
4
Join an Array of Strings
Turn your array into a serialized String
3:33
5
Data from JSON
Load data from a JSON file into your SwiftUI application
5:08
6
HTTP Request
Create an HTTP Get Request to fetch data from an API
6:31
7
WKWebView
Integrate an HTML page into your SwiftUI application using WKWebView and by converting Markdown into HTML
5:25
8
Code Highlighting in a WebView
Use Highlight.js to convert your code blocks into beautiful highlighted code in a WebView
5:11
9
Test for Production in the Simulator
Build your app on Release scheme to test for production
1:43
10
Debug Performance in a WebView
Enable Safari's WebInspector to debug the performance of a WebView in your application
1:57
11
Debug a Crash Log
Learn how to debug a crash log from App Store Connect in Xcode
2:22
12
Simulate a Bad Network
Test your SwiftUI application by simulating a bad network connection with Network Link Conditionner
2:11
13
Archive a Build in Xcode
Archive a build for beta testing or to release in the App Store
1:28
14
Apollo GraphQL Part I
Install Apollo GraphQL in your project to fetch data from an API
6:21
15
Apollo GraphQL Part 2
Make a network call to fetch your data and process it into your own data type
6:43
16
Apollo GraphQL Part 3
Display the data fetched with Apollo GraphQL in your View
5:08
17
Configuration Files in Xcode
Create configuration files and add variables depending on the environment - development or production
4:35
18
App Review
Request an app review from your user for the AppStore
5:43
19
ImagePicker
Create an ImagePicker to choose a photo from the library or take a photo from the camera
5:06
20
Compress a UIImage
Compress a UIImage by converting it to JPEG, reducing its size and quality
3:32
21
Firebase Storage
Upload, delete and list files in Firebase Storage
11:11
22
Search Feature
Implement a search feature to filter through your content in your SwiftUI application
9:13
23
Push Notifications Part 1
Set up Firebase Cloud Messaging as a provider server to send push notifications to your users
5:59
24
Push Notifications Part 2
Create an AppDelegate to ask permission to send push notifications using Apple Push Notifications service and Firebase Cloud Messaging
6:30
25
Push Notifications Part 3
Tie everything together and test your push notifications feature in production
6:13
26
Network Connection
Verify the network connection of your user to perform tasks depending on their network's reachability
6:49
27
Download Files Locally Part 1
Download videos and files locally so users can watch them offline
6:05
28
Download Files Locally Part 2
Learn how to use the DownloadManager class in your views for offline video viewing
6:02
29
Offline Data with Realm
Save your SwiftUI data into a Realm so users can access them offline
10:20
30
HTTP Request with Async Await
Create an HTTP get request function using async await
6:11
31
Xcode Cloud
Automate workflows with Xcode Cloud
9:23
32
SceneStorage and TabView
Use @SceneStorage with TabView for better user experience on iPad
3:52
33
Network Connection Observer
Observe the network connection state using NWPathMonitor
4:37
34
Apollo GraphQL Caching
Cache data for offline availability with Apollo GraphQL
9:42
35
Create a model from an API response
Learn how to create a SwiftUI model out of the response body of an API
5:37
36
Multiple type variables in Swift
Make your models conform to the same protocol to create multiple type variables
4:23
37
Parsing Data with SwiftyJSON
Make API calls and easily parse data with this JSON package
9:36
38
ShazamKit
Build a simple Shazam clone and perform music recognition
12:38
39
Firebase Remote Config
Deliver changes to your app on the fly remotely
9:05
Meet the instructor
We all try to be consistent with our way of teaching step-by-step, providing source files and prioritizing design in our courses.
Stephanie Diep
iOS and Web developer
Developing web and mobile applications while learning new techniques everyday
7 courses - 36 hours

Build Quick Apps with SwiftUI
Apply your Swift and SwiftUI knowledge by building real, quick and various applications from scratch
11 hrs

Advanced React Hooks Handbook
An extensive series of tutorials covering advanced topics related to React hooks, with a main focus on backend and logic to take your React skills to the next level
3 hrs

SwiftUI Concurrency
Concurrency, swipe actions, search feature, AttributedStrings and accessibility were concepts discussed at WWDC21. This course explores all these topics, in addition to data hosting in Contentful and data fetching using Apollo GraphQL
3 hrs

SwiftUI Combine and Data
Learn about Combine, the MVVM architecture, data, notifications and performance hands-on by creating a beautiful SwiftUI application
3 hrs

SwiftUI Advanced Handbook
An extensive series of tutorials covering advanced topics related to SwiftUI, with a main focus on backend and logic to take your SwiftUI skills to the next level
4 hrs

React Hooks Handbook
An exhaustive catalog of React tutorials covering hooks, styling and some more advanced topics
5 hrs

SwiftUI Handbook
A comprehensive series of tutorials covering Xcode, SwiftUI and all the layout and development techniques
7 hrs
