React Course for Designers with Codux
Add to favorites
Codux is designed to bridge the gap between designers and developers
Play video
Build a React Site from Figma to Codux
1
React Course for Designers with Codux
5:13
2
Create a Basic Layout from Figma to Codux
10:33
3
Figma to CSS Code and Dev Mode
9:02
4
Figma Variables to Code and Responsive Layout
12:45
5
Multiple React Components in Codux
8:41
6
Figma Design to React Code
12:30
7
Breakpoints using CSS Media Queries
7:51
8
Creating a Drawer Menu with Component States in React
10:50
9
Code Editors, AI Tools and Github Copilot
14:51
10
CSS Transitions and Animations
9:27
11
Loop Data and Reusable Component with Props
14:58
12
Dark Mode Variables and Animations
5:25
13
Multiple Pages with React Router and Codux
6:26
14
SEO and Publishing
10:11
Meet Codux
Codux is less intimidating for designers than code editors. It lets you handle styling visually, like Xcode, using boards and components. You can create a full site without touching code, except for optional CSS and routing. Codux organizes projects visually, making it easier to navigate and reuse components. My tutorial shows how it works—worth trying if code-centric tools are too much.

Codux offers a user-friendly environment for designers, bridging the gap between design and code. Here's why it's worth considering:
- Visual Styling: Codux allows you to handle boards and components visually, similar to Xcode, making it less intimidating than diving straight into VSCode.
- Minimal Coding Required: You can create an entire site without touching code, except for optional CSS and necessary routing for multiple pages. This makes it accessible for designers who prefer a visual approach.
- Full React Support: Since it's a full React site, you have the flexibility to expand and customize as needed.
- Organized Code Projects: Codux helps you organize your projects visually, making it easier to navigate large projects, especially in a team environment with both designers and developers.
- Reusable Components: The platform encourages reuse of components, promoting cleaner and more efficient code management.
- UI Elements and Templates: Codux provides various UI elements and templates to help you get started quickly.
This Course

In this course, you’ll build a website from scratch using Codux, starting with a Figma template. Learn to design, extract CSS, and understand Codux features. Collaborate with developers, set up multiple pages with React Router, and implement responsive designs with media queries. Create dynamic components with props and follow best practices for effective collaboration and website creation.
- Final site: https://nimble-elf-f60a07.netlify.app
- Figma Template: https://www.dropbox.com/s/cc0of4gwk8gwtg8/Codux%20Course.zip?dl=0
- DesignCode UI: https://www.figma.com/community/file/1316701892522528301
- Github: https://github.com/MengTo/codux-course
Preparing Your Responsive Figma Design

Creating fully responsive sites in Figma is now easier with features like auto layout wrap and min/max constraints, ensuring designs look great on any device. Code export plugins such as Dev Mode, Figma to Code, Anima, and Locofy simplify the transition from design to development by handling much of the CSS work.
To ensure your Figma design is ready for responsive web development, follow these guidelines:
- Proper Naming Conventions: Name all text layers appropriately. Ensure all groups and subgroups are named correctly to avoid fallback to generic class names.
- Use Frames for Containers: Do not use groups for containers; always use frames. Frames provide more control over layout and responsiveness.
- Inner Elements: Use the "Fill" setting for inner elements instead of fixed sizes or "Hug" settings. This ensures elements adapt properly within their containers.
- Design Readiness Checklist: Utilize the Local Lightning plugin to review your design. The plugin provides suggestions and actions to ensure your design is fully prepared for responsive web development.
How to Prepare Your Figma Designs for Code Export
Frames:
- Use frames to structure your design.
- Employ nested frames for organization.
- Apply absolute positioning for precise element placement.
Constraints:
- Set min/max constraints for responsive resizing.
- Use responsive constraints to pin elements within frames.
Auto-Layout:
- Utilize fill/hug content settings for flexible element resizing.
- Implement auto-layout wrap for clean layouts across different screens.
- Define gaps and use the "space between" setting for consistent spacing.
Additional Tips:
- Use component variants for different states.
- Define styles and variables for consistency.
- Maintain clear naming conventions.
Utilizing Code Export Tools:
- Dev Mode: Export CSS styles and assets.
- CSS Variables Generator Plugin (Free): Generate variables for consistent design.
- Figma to Code Plugin (Free): Export HTML/CSS/Tailwind/JSX, Flutter, and SwiftUI.
- Anima (Paid): Export production-ready HTML/CSS/React/Vue code.
- Framer: Launch responsive websites directly from Figma.
- Locofy.ai: Export clean, production-ready code.
By following these steps, you can ensure your Figma design is well-structured and optimized for responsive web implementation.
Download Codux

Codux is readily available for both Mac and Windows platforms, catering to a wide range of users and environments. To start using Codux:
- Visit the Codux website.
- Click on to the Download button.
- Choose the version appropriate for your operating system.
- Follow the installation instructions to get Codux set up on your machine.
Codux Templates
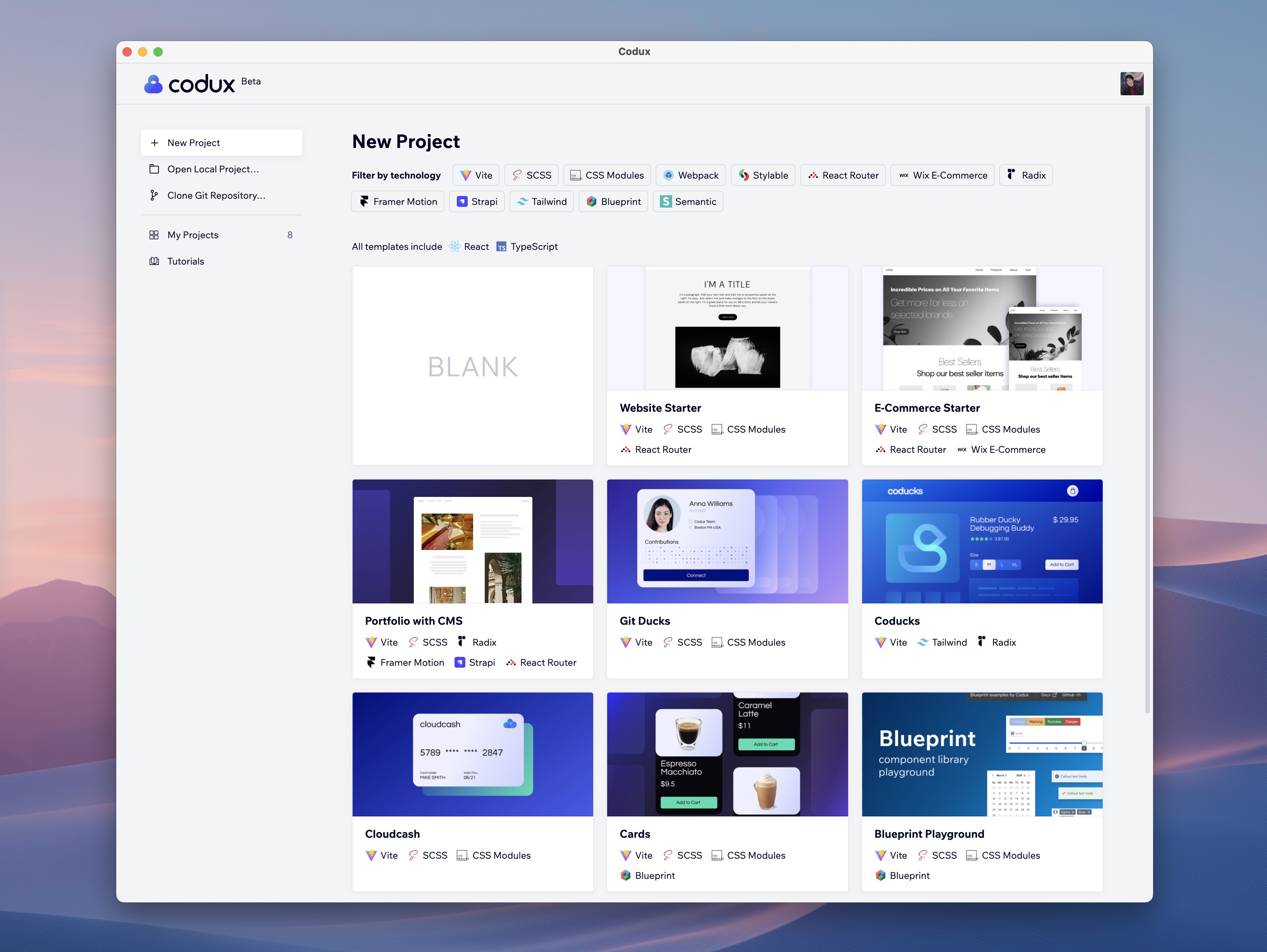
To help you jumpstart your projects, Codux provides a variety of templates. Each template is designed with a specific purpose in mind, allowing you to choose one that best fits your project’s needs:
- Blank Template: Ideal for those who want to start from scratch and build their design with complete creative freedom.
- Starter Template: Contains the essential components and layouts to help you get started quickly, perfect for general web development projects.
- E-Commerce Starter: Tailored for e-commerce projects, this template includes layouts and components that are commonly used in online stores, such as product listings and shopping carts.
- Various Sample Projects: Explore different design possibilities with templates designed for content management systems, card layouts, Semantic UI frameworks, and more. These templates provide a practical starting point and can be customized to suit your project requirements.
Using these templates, you can significantly reduce development time and start with a solid foundation, whether you are building a simple site or a complex web application.
Setting Up Your Project
Getting started with Codux is straightforward and intuitive. It provides a user-friendly interface for designers to create and manage projects visually. Follow these steps to set up your first project:
- Start with Codux: Open Codux and set up a new project.
- Select Blank Template: Choose the Blank template.
- Edit Initial Design: Double-click on the App board to start editing the initial design.
Boards and Components in Codux
Codux provides a powerful way to manage and test your components using boards. Here’s a brief overview:
- Boards: Boards are isolated environments where you can render components with various property values, states, and settings. They allow you to test and edit components along with HTML elements, fully mocking how the component will be used in your app.
- Components: Components in Codux render based on the board's code settings. Board files have the .board.tsx extension and can be edited using Codux's built-in code editor or an external IDE. You can also create new boards visually in Codux. Changes to a board are immediately visible and saved to the board's code file.
Style Management
- CSS Modules: Apply styles to individual components or boards without them cascading to other areas. This ensures that styles are scoped locally, avoiding unintended global style conflicts.
- Global Styles: Manage consistent themes across your project by defining global styles for variables, colors, fonts, etc. Global styles ensure a cohesive look and feel throughout your project.
- Reset CSS: Use a Reset CSS template to normalize and standardize default browser styles, creating a consistent foundation for your project’s custom styles. This helps eliminate browser inconsistencies and simplifies cross-browser compatibility.
// index.css
@import url('https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Manrope:wght@400;500;600;700&display=swap');
:root {
/* font */
--font: Manrope;
/* font sizes */
--subheadline-semibold-size: 15px;
--caption-2-regular-size: 11px;
--headline-medium-size: 20px;
--body-regular-size: 16px;
--headings-heading-5-size: 24px;
--headings-heading-2-size: 50px;
--small-regular-size: 12px;
/* Animation */
--transition: transition: 0.8s cubic-bezier(0.2, 0.8, 0.2, 1);
/* Font Size */
--small: 12px;
--caption: 13px;
--footnote: 14px;
--body: 16px;
--body-large: 18px;
--headline: 20px;
--heading-5: 24px;
--heading-4: 30px;
--heading-3: 40px;
--heading-2: 50px;
--heading-1: 60px;
/* Colors */
--background-primary: rgb(255, 255, 255);
--background-secondary: rgb(255, 255, 255, 0.1);
--background-tertiary: rgb(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
--button-foreground: rgb(255, 255, 255);
--container-background: rgb(255, 255, 255, 0.6);
--container-background-recessed: rgb(255, 255, 255, 0.9);
--container-background-secondary: rgb(255, 255, 255, 0.1);
--container-background-tertiary: rgb(255, 255, 255, 0.9);
--container-border: rgb(255, 255, 255, 0.5);
--container-border-secondary: rgb(255, 255, 255, 0.2);
--container-divider: rgb(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
--container-divider-secondary: rgb(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
--foreground-primary: rgb(0, 0, 0);
--foreground-secondary: rgb(0, 0, 0, 0.7);
--foreground-tertiary: rgb(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
}
body {
background-color: var(--background-primary);
}Dark Mode Variables
Dark mode variables enable your project to adapt to users’ dark mode preferences, providing a more comfortable viewing experience in low-light environments. Using the @media (prefers-color-scheme: dark) media query, you can define a set of CSS variables specifically for dark mode.
@media (prefers-color-scheme: dark) {
--background-primary: rgb(0, 0, 0);
--background-secondary: rgb(0, 0, 0 , 0.1);
--background-tertiary: rgb(255, 255, 255 , 0.1);
--button-foreground: rgb(255, 255, 255);
--container-background: rgb(0, 0, 0 , 0.6);
--container-background-recessed: rgb(0, 0, 0 , 0.2);
--container-background-secondary: rgb(0, 0, 0 , 0.1);
--container-background-tertiary: rgb(255, 255, 255 , 0.1);
--container-border: rgb(255, 255, 255 , 0.1);
--container-border-secondary: rgb(255, 255, 255 , 0.1);
--container-divider: rgb(255, 255, 255 , 0.1);
--container-divider-secondary: rgb(255, 255, 255 , 0.2);
--foreground-primary: rgb(255, 255, 255);
--foreground-secondary: rgb(255, 255, 255 , 0.7);
--foreground-tertiary: rgb(255, 255, 255 , 0.5);
}Dark Mode SVG Images with Invert Filter

To ensure SVG images look appropriate in dark mode, you can use the invert filter. This approach helps maintain visibility and consistency of images without needing separate dark mode assets. By applying the invert filter within the @media (prefers-color-scheme: dark) media query, your SVG images will invert their colors, making them suitable for dark backgrounds.
@media (prefers-color-scheme: dark) {
img {
filter: invert(1);
}
}Breakpoints and CSS Media Queries
To adjust the padding for different screen widths, you can use the following media queries:
// HomePage .root, BrowsePage .root
@media(max-width: 800px) {
padding: 30px;
}
@media (max-width: 500px) {
padding: 20px;
}For adjusting title sizes based on screen width:
// Header
.logoText {
display: block;
@media (max-width: 800px) {
display: none;
}
}Button Transition and Hover
Adding smooth transitions and hover effects enhances the user experience by providing visual feedback and making interactions feel more responsive. In Codux, you can define transition properties and hover states for elements to achieve this.
transition: 0.8s cubic-bezier(0.2, 0.8, 0.2, 1);
&:hover {
background-color: var(--container-divider-secondary);
border-color: var(--container-divider-secondary);
}Appear Animation
Adding appear animations can create a dynamic and engaging user experience by gradually revealing elements on the screen. This technique involves animating elements from an initial state of opacity and position to their final visible state.
.title,
.subtitle,
.text,
.buttons,
.image {
opacity: 0;
animation: fadeIn 1s cubic-bezier(0.2, 0.8, 0.2, 1) forwards;
}
.title {
animation-delay: 0.1s;
}
.subtitle {
animation-delay: 0.2s;
}
.text {
animation-delay: 0.3s;
}
.buttons {
animation-delay: 0.4s;
}
.image {
animation-delay: 0.5s;
}
@keyframes fadeIn {
from {
opacity: 0;
transform: translateY(-20px);
}
to {
opacity: 1;
transform: translateY(0);
}
}Handle Drawer Visibility with States
To control the drawer’s visibility, use React’s state management. Define a state variable to track whether the drawer is visible or not. Create a function to toggle this state when the hamburger menu is clicked.
const [isDrawerVisible, setDrawerVisible] = useState(false);
const toggleDrawer = () => {
setDrawerVisible(!isDrawerVisible);
};Add a drawer menu button to your header. This button will trigger the drawer’s visibility toggle function. When the button is clicked, the state variable updates, and the drawer appears or hides based on this state.
<a className={styles.buttonCircle} onClick={toggleDrawer}>
<img src={MenuAlignLeftDescSvg} alt="" height="24px" width="24px" />
</a>React Helmet
React Helmet is a library that allows you to manage changes to the document head in a React application. This includes updating the title, meta tags, and other elements, providing better control over SEO and user experience.
To use React Helmet, install the library and its TypeScript definitions:
npm install react-helmet
npm install --save-dev @types/react-helmetImport React Helmet and use it within your components to define head elements:
import { Helmet } from 'react-helmet';
<Helmet>
<title>Figma UI Kit and design system for iOS</title>
<meta name="description" content="Create iOS apps faster with our extensive Figma UI kit. It offers adaptive components, font/color variables, dynamic type sizes, and both light and dark mode designs." />
<meta name="keywords" content="Figma UI Kit, iOS App Design, UI Design" />
</Helmet>Multiple Pages with React Router and Codux

Creating multiple pages in a React application using React Router with Codux involves setting up navigation links, configuring the router, and defining routes. This approach allows seamless navigation between different components in your project.
- Install react-router-dom
First, install the react-router-dom package to enable routing capabilities in your React application:
npm install react-router-dom- Set up the Link in Navigation
In your navigation component, use the Link component from react-router-dom to create navigable links:
// Header.tsx
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom';
<Link to={'/'}><Link>- Set Routes in App Component
Ensure your routes are properly defined in the App component and that the router is used within the relevant components:
// App.tsx
import { Route, Routes } from 'react-router-dom';
import { MemoryRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
function App() {
return (
<MemoryRouter>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<HomePage />} />
<Route path="/browse" element={<BrowsePage />} />
</Routes>
</MemoryRouter>
);
}- Set MemoryRouter in App
Wrap your application in MemoryRouter to manage the routing in memory, ideal for applications where you don’t need a persistent URL (like in Codux). App.tsx and the boards won't load in your real application, but is necessary in Codux.
// Header board, HomePage board, BrowsePage board
import { MemoryRouter } from 'react-router-dom";
<MemoryRouter><Header />
<Header />
</MemoryRouter>- Real Application with Routing
In a real application, you would typically use BrowserRouter to handle routing, enabling persistent URLs and better handling of the browser’s history:
// main.tsx
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Routes, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
<React.StrictMode>
<Router>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<HomePage />} />
<Route path="/browse" element={<BrowsePage />} />
<Route path="/updates" element={<UpdatesPage />} />
</Routes>
</Router>
</React.StrictMode>,GitHub Integration in Codux
Committing Changes
In Codux, committing your changes is straightforward and similar to how you manage version history in Figma. Here’s how you do it:
- Make Your Edits: Work on your designs as usual. Every change you make can be committed, ensuring you have a log of your progress.
- Commit Your Changes: Once you’re ready, commit your changes to your repository. This action saves a snapshot of your current work.
Publishing Your Website
Once your project is ready for deployment, you can use Netlify or Vercel to publish it. Here’s a step-by-step guide:

Connecting to GitHub
- Sign Up/Log In: Create an account or log in to Netlify or Vercel.
-
Connect to GitHub: Link your Netlify or Vercel account to your GitHub repository.
- In Netlify: Navigate to "New site from Git" and choose GitHub.
- In Vercel: Click on "Add New Project" and select GitHub.
- Select Your Repository: Choose the repository you want to deploy.
- Configure Build Settings: Set the build settings for your React project. Netlify and Vercel often auto-detect the settings, but you can adjust them if needed.
- Deploy: Click on "Deploy Site" (Netlify) or "Deploy" (Vercel). Your website will be built and published.
Resources to Learn Codux
- Video Tutorials: Official tutorials made by Codux.
- Community: Join Discord groups for support and tips.
- Playgrounds: Explore real-world examples.
- Social Media: Follow Codux on Twitter and YouTube for updates and tutorials.
Templates and source code
Download source files
Download the videos and assets to refer and learn offline without interuption.
Design template
Source code for all sections
Video files, ePub and subtitles
Assets
Design
Videos
Codux Course.fig
1
React Course for Designers with Codux
Codux is designed to bridge the gap between designers and developers
5:13
2
Create a Basic Layout from Figma to Codux
Creating your first layout in Codux is an exciting journey into the world of visual web development
10:33
3
Figma to CSS Code and Dev Mode
Extracting CSS code from Figma and implementing it in Codux is straightforward
9:02
4
Figma Variables to Code and Responsive Layout
Variables in CSS are essential for maintaining consistency across your design projects
12:45
5
Multiple React Components in Codux
Creating reusable components in Codux
8:41
6
Figma Design to React Code
Exporting Figma designs to React code is now more accessible than ever
12:30
7
Breakpoints using CSS Media Queries
Create responsive designs that adapt to different screen sizes
7:51
8
Creating a Drawer Menu with Component States in React
Setting up components, styling them, and managing visibility with props and states
10:50
9
Code Editors, AI Tools and Github Copilot
Using a code editor like Visual Studio Code (VS Code) or Zed can make web development easier
14:51
10
CSS Transitions and Animations
Make your web pages more engaging with CSS animations in Codux
9:27
11
Loop Data and Reusable Component with Props
Building a reusable image gallery component in Codux
14:58
12
Dark Mode Variables and Animations
Step-by-step guide to applying dark mode variables
5:25
13
Multiple Pages with React Router and Codux
React Router allows you to navigate between multiple pages
6:26
14
SEO and Publishing
Add SEO using React Helmet and publish to Netlify
10:11
Meet the instructor
We all try to be consistent with our way of teaching step-by-step, providing source files and prioritizing design in our courses.
Meng To
I design, code and write
Meng To is the author of Design+Code. Meng started off his career as a self-taught designer from Montreal and eventually traveled around the world for 2 years as his US VISA was denied. During his travels, he wrote a book which now has 35,000 readers.
40 courses - 194 hours

Master AI Prompting for Stunning UI
Learn how to leverage AI tools like Aura for creating beautiful designs, working with templates, and experimenting with advanced prompts. A concise guide for designers and developers to level up their skills.
10 hrs

Build SwiftUI apps for iOS 18 with Cursor and Xcode
In this course, we'll explore the exciting new features of SwiftUI 6 and Xcode 16 for building iOS 18 apps. From mesh gradients and text animations to ripple effects, you'll learn how to create polished, highly custom apps using the latest workflows. We'll also dive into using Cursor and Claude AI for AI-driven coding, helping you start strong and customize your apps.
5 hrs

Create your Dream Apps with Cursor and Claude AI
Learn to build your dream web apps from the ground up using Cursor, Claude AI, and a suite of powerful AI tools. This course covers everything you need, including React for frontend development, Firebase for backend integration, and Stripe for handling payments. You’ll also dive into advanced AI tools like Claude Artifacts, Galileo AI, v0.dev for UI, Ideogram for design generation, and Cursor Composer for full-scale development.
6 hrs

Build a React Site from Figma to Codux
In this course, you'll learn to build a website from scratch using Codux, starting with a Figma template. You’ll master responsive design, collaborate with developers on a real React project, export CSS from Figma using Locofy, set up breakpoints with media queries, add CSS animations, improve SEO, create multiple pages with React Router, and publish your site. By following best practices, you’ll bridge design and development, improve your web design skills.
2 hrs

Create 3D UI for iOS and visionOS in Spline
Comprehensive 3D Design Course: From Basics to Advanced Techniques for iOS and visionOS using SwiftUI
3 hrs

Master No-Code Web Design with Framer
In this free Framer course, you'll learn to create modern, user-friendly interfaces. Start with dark mode and glass designs, then move from Figma to Framer, using vectors and auto layout for responsive websites. Add animations, interactive buttons, and custom components with code. Finally, you'll craft a design system suitable for teamwork or solo projects, all in a straightforward and practical approach.
4 hrs

Build SwiftUI Apps for iOS 17
In this course, we’ll be exploring the fresh and exciting features of SwiftUI 5! As we craft a variety of iOS apps from the ground up, we'll delve deep into the treasure trove that is SwiftUI's user interface, interactions, and animations.
4 hrs

Build Beautiful Apps with GPT-4 and Midjourney
Design and develop apps using GPT-4 and Midjourney with prompts for SwiftUI, React, CSS, app concepts, icons, and copywriting
4 hrs

Build SwiftUI apps for iOS 16
Create animated and interactive apps using new iOS 16 techniques using SwiftUI 4 and Xcode 14
5 hrs

Build a 3D Site Without Code with Framer
Design and publish a responsive site with 3D animation without writing a single line of code
3 hrs

Create 3D Site with Spline and React
Design and code a landing page with an interactive 3D asset using Spline and CodeSandbox
1 hrs

Build an Animated App with Rive and SwiftUI
Design and code an iOS app with Rive animated assets, icon animations, custom layouts and interactions
3 hrs

Build a SwiftUI app for iOS 15 Part 3
Design and code a SwiftUI 3 app with custom layouts, animations and gestures using Xcode 13, SF Symbols 3, Canvas, Concurrency, Searchable and a whole lot more
4 hrs

Build a SwiftUI app for iOS 15 Part 2
Design and code a SwiftUI 3 app with custom layouts, animations and gestures using Xcode 13, SF Symbols 3, Canvas, Concurrency, Searchable and a whole lot more
3 hrs

Build a SwiftUI app for iOS 15
Design and code a SwiftUI 3 app with custom layouts, animations and gestures using Xcode 13, SF Symbols 3, Canvas, Concurrency, Searchable and a whole lot more
4 hrs

React Livestreams
Learn how we can use React Hooks to build web apps using libraries, tools, apis and frameworks
4 hrs

Design Founder Livestreams
A journey on how we built DesignCode covering product design, management, analytics, revenue and a good dose of learning from our successes and failures
2 hrs

SwiftUI Advanced Handbook
An extensive series of tutorials covering advanced topics related to SwiftUI, with a main focus on backend and logic to take your SwiftUI skills to the next level
4 hrs

iOS Design Handbook
A complete guide to designing for iOS 14 with videos, examples and design files
2 hrs

SwiftUI Handbook
A comprehensive series of tutorials covering Xcode, SwiftUI and all the layout and development techniques
7 hrs

Build a web app with React Hooks
Learn how we built the new Design+Code site with React Hooks using Gatsby, Netlify, and advanced CSS techniques with Styled Components.
4 hrs

UI Design Handbook
A comprehensive guide to the best tips and tricks for UI design. Free tutorials for learning user interface design.
2 hrs

Figma Handbook
A comprehensive guide to the best tips and tricks in Figma. Not affiliated with or endorsed by Figma, Inc.
6 hrs

SwiftUI for iOS 14
Build a multi-platform app from scratch using the new techniques in iOS 14. We'll use the Sidebar and Lazy Grids to make the layout adaptive for iOS, iPadOS, macOS Big Sur and we'll learn the new Matched Geometry Effect to create beautiful transitions between screens without the complexity. This course is beginner-friendly and is taught step-by-step in a video format.
3 hrs

SwiftUI Livestreams
This is a compilation of the SwiftUI live streams hosted by Meng. Over there he talks and teaches how to use design systems, typography, navigation, iOS 14 Design, prototyping, animation and Developer Handoff.
19 hrs

UI Design Livestreams
This is a compilation of the UI live streams hosted by Meng. Over there he talks and teaches how to use design systems, typography, navigation, iOS 14 Design, prototyping, animation and Developer Handoff.
26 hrs

UI Design for Developers
In this course we'll learn how to use design systems, set up break points, typography, spacing, navigation, size rules for adapting to the iPad, mobile and web versions, and different techniques that translate well from design to code.
3 hrs

Build an app with SwiftUI Part 3
This course was written for designers and developers who are passionate about design and about building real apps for iOS, iPadOS, macOS, tvOS and watchOS. SwiftUI works across all of those platforms. While the code is not a one-size-fits-all, the controls and techniques involved can apply to all platforms. It is beginner-friendly, but it is also packed with design tricks and cool workflows about building the best UIs and interactions.
4 hrs

Build an app with SwiftUI Part 2
This course was written for designers and developers who are passionate about design and about building real apps for iOS, iPadOS, macOS, tvOS and watchOS. SwiftUI works across all of those platforms. While the code is not a one-size-fits-all, the controls and techniques involved can apply to all platforms. It is beginner-friendly, but it is also packed with design tricks and cool workflows about building the best UIs and interactions.
4 hrs

Build a full site in Webflow
Webflow is a design tool that can build production-ready experiences without code. You can implement CSS-driven adaptive layouts, build complex interactions and deploy all in one tool. Webflow also comes with a built-in content management system (CMS) and Ecommerce for creating a purchase experience without the need of third-party tools.
3 hrs

Advanced Prototyping in ProtoPie
ProtoPie is a cross-platform prototyping tool that creates prototypes nearly as powerful as those made with code, with half of the efforts, and zero code. It's perfect for designers who want to quickly experiment with advanced interactions using variables, conditions, sensors and more.
3 hrs

Build an app with SwiftUI Part 1
This course was written for designers and developers who are passionate about design and about building real apps for iOS, iPadOS, macOS, tvOS and watchOS. SwiftUI works across all of those platforms. While the code is not a one-size-fits-all, the controls and techniques involved can apply to all platforms. It is beginner-friendly, but it is also packed with design tricks and cool workflows about building the best UIs and interactions.
4 hrs

React Native for Designers Part 2
React Native is a popular Javascript framework that builds on top of React by using native components to create a real mobile app indistinguishable from one made using Xcode or Android Studio. The main difference with native development is that you get to use CSS, hot-reload, Javascript and other familiar techniques that the Web has grown over the past decades. Most importantly, you're building for both iOS and Android using the same codebase.
3 hrs

React Native for Designers
React Native is a popular Javascript framework that builds on top of React by using native components to create a real mobile app indistinguishable from one made using Xcode or Android Studio. The main difference with native development is that you get to use CSS, hot-reload, Javascript and other familiar techniques that the Web has grown over the past decades. Most importantly, you're building for both iOS and Android using the same codebase.
5 hrs

Design System in Figma
Learn how to use and design a collaborative and powerful design system in Figma. Design Systems provide a shared library of reusable components and guidelines and that will let you build products much faster
3 hrs

React for Designers
Learn how to build a modern site using React and the most efficient libraries to get your site/product online. Get familiar with Grid CSS, animations, interactions, dynamic data with Contentful and deploying your site with Netlify.
3 hrs

Swift Advanced
Learn Swift a robust and intuitive programming language created by Apple for building apps for iOS, Mac, Apple TV and Apple Watch
9 hrs

Learn Swift
Learn Swift a robust and intuitive programming language created by Apple for building apps for iOS, Mac, Apple TV and Apple Watch
4 hrs

Learn Sketch
Learn Sketch a design tool entirely vector-based and focused on user interface design
5 hrs

Learn iOS 11 Design
Learn colors, typography and layout for iOS 8
1 hrs
